FAQ
-
QWhat is SJTW cable?ASJTW is a designation in the US National Electrical Code (NEC) for a special type of extension cord (power cord). It represents a component of S (Service Cord), J (Junior/18-30 AWG), T (Thermoplastic insulation), and W (Weather-resistant). It typically features a full copper conductor and double-layer vinyl insulation, suitable for indoor and outdoor environments with humidity, sunlight, and abrasion. It is waterproof and weather-resistant.
SJTW cable features:
Applications: Indoor and outdoor power supply for household appliances, extension cords, industrial equipment, etc.
Material: 100% pure copper conductor, durable vinyl (PVC) insulation.
Performance: Soft, flexible, waterproof, weather-resistant, oil-resistant, moisture-resistant, and abrasion-resistant.
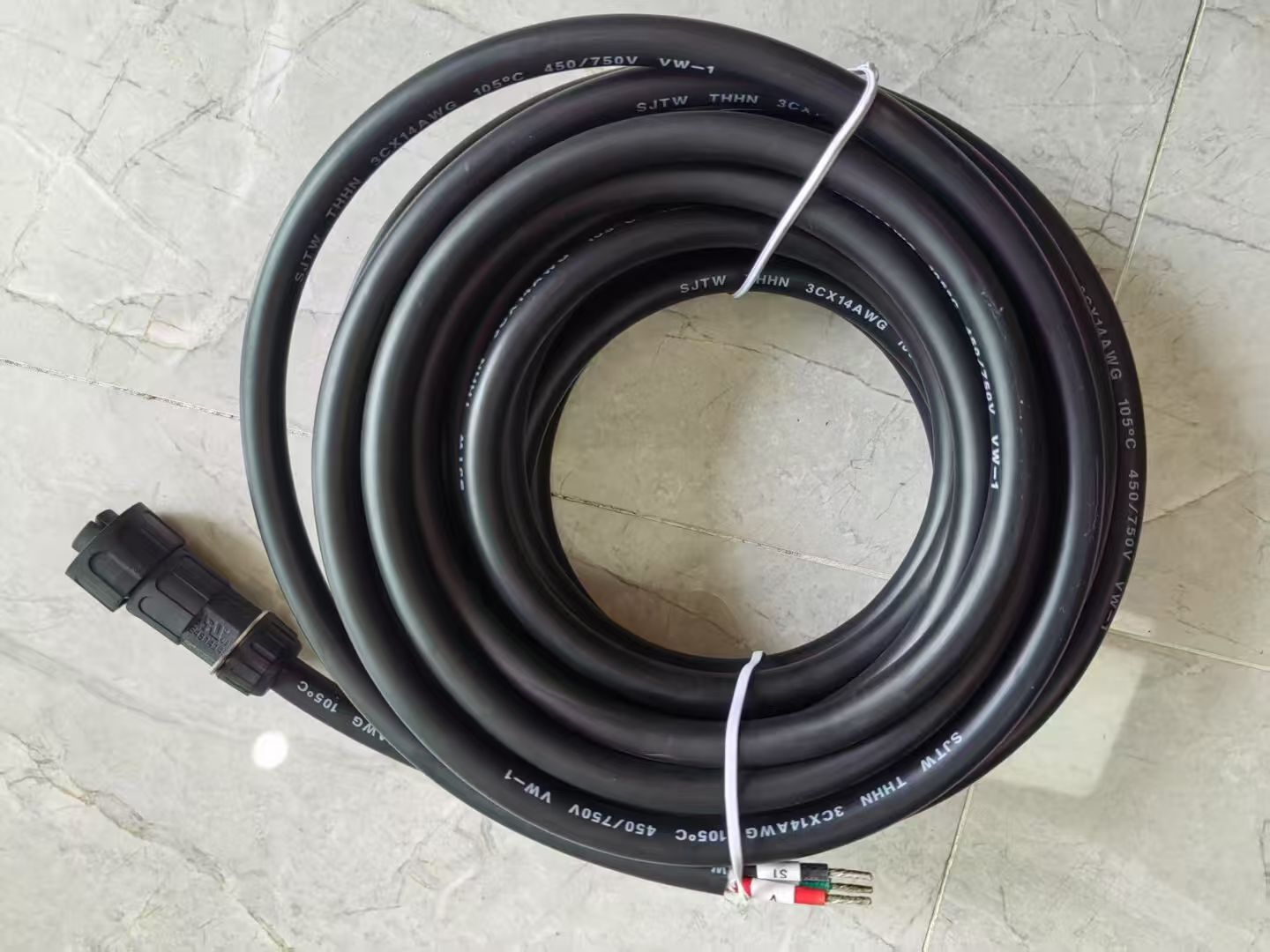

Meaning of markings:
S: Service Cord/Extension Cord
J: Junior/18-30 AWG (smaller wire gauge)
T: Thermoplastic insulation
W: Weather-resistant, suitable for humid environments.
In summary: SJTW cable is a robust, durable, and reliable extension cord, particularly suitable for outdoor or damp environments requiring waterproofing and weather resistance. -
QWhat is the difference between cable accessories and cable fittings?ACable accessories are functional components used to connect, terminate, or insulate cables, ensuring the safe and stable operation of the cable system, such as cable joints and terminations.
Cable fittings are mainly mechanical parts that fix, support, or protect cables and accessories, like cable clamps and brackets, playing an auxiliary role in installation and fixation. -
QWhat is the difference between concentric cable and coaxial cable?AA concentric cable refers to a cable structure where conductors are arranged concentrically (sharing the same center axis), which is a general structural description.
A coaxial cable is a specific type of concentric cable, typically consisting of an inner conductor, insulating layer, outer conductor (shield), and outer sheath, designed for high-frequency signal transmission with strong anti-interference ability. -
QWhat is RS485 cable?ARS485 cable is a kind of communication cable specially designed for RS485 bus communication. Here are its key points:
Application
It is mainly used in the RS485 bus, which is a widely used serial communication standard in the field of industrial automation. It is suitable for occasions requiring long-distance data transmission and multi-point communication, such as factory automation, building automation, and security systems.
Features
- It usually adopts a twisted pair structure, which can effectively reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, and improve the stability and reliability of data transmission.
- It has the characteristics of long transmission distance. In some cases, the transmission distance can reach several hundred meters or even longer.
- It supports multi-point communication, and multiple devices can be connected to the same RS485 bus for communication.
Interface
The common interface types include terminal blocks, DB9 connectors, etc., which are used to connect devices such as controllers and sensors. -
QWhat is OPGW?AOPGW is an abbreviation for Optical Fiber Composite Overhead Ground Wire. It is a special cable that combines optical fibers with a grounding wire, mainly used in overhead power transmission lines. Here are its key features and functions:
Structure:
It consists of optical fibers enclosed in a metal sheath, surrounded by a stranded wire (usually made of aluminum alloy, steel, etc.) to form a cable that can be used as both a grounding wire and an optical communication medium.
Functions:
- Grounding and Lightning Protection: As an overhead ground wire, it can protect the power line from lightning strikes and provide a grounding path.
- Optical Communication: The optical fibers inside enable high-speed data transmission, supporting power system communication, monitoring, and control.
Advantages:
It integrates power grounding and communication functions, saving installation space and costs, and is widely used in high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage power grids. -
QWhat is power distribution?APower distribution refers to the final stage in the delivery of electric power from generation sources to end users, such as homes, businesses, and industries. It involves the network of substations, transformers, and power lines that carry electricity from the transmission system and distribute it to consumers. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. Generation: Electricity is produced at power plants using various energy sources like coal, natural gas, nuclear, hydro, wind, or solar.
2. Transmission: High-voltage transmission lines transport electricity over long distances from power plants to substations. This is done at high voltages to reduce energy loss.
3. Substations: At substations, transformers reduce the high voltage electricity to lower levels suitable for distribution.
4. Distribution: The lower voltage electricity is then sent through a network of distribution lines to reach local areas. These lines can be overhead or underground.
5. Service Lines: Finally, service lines deliver electricity from the distribution lines directly to homes and businesses. Transformers near the end-use locations further reduce the voltage to the levels needed by appliances and equipment.
The power distribution system is crucial for ensuring that electricity is delivered reliably and efficiently to meet the demands of consumers. It includes various components like distribution transformers, circuit breakers, and meters, and is managed by utility companies or local distribution networks