22
Jan
What is AAAC
Share:
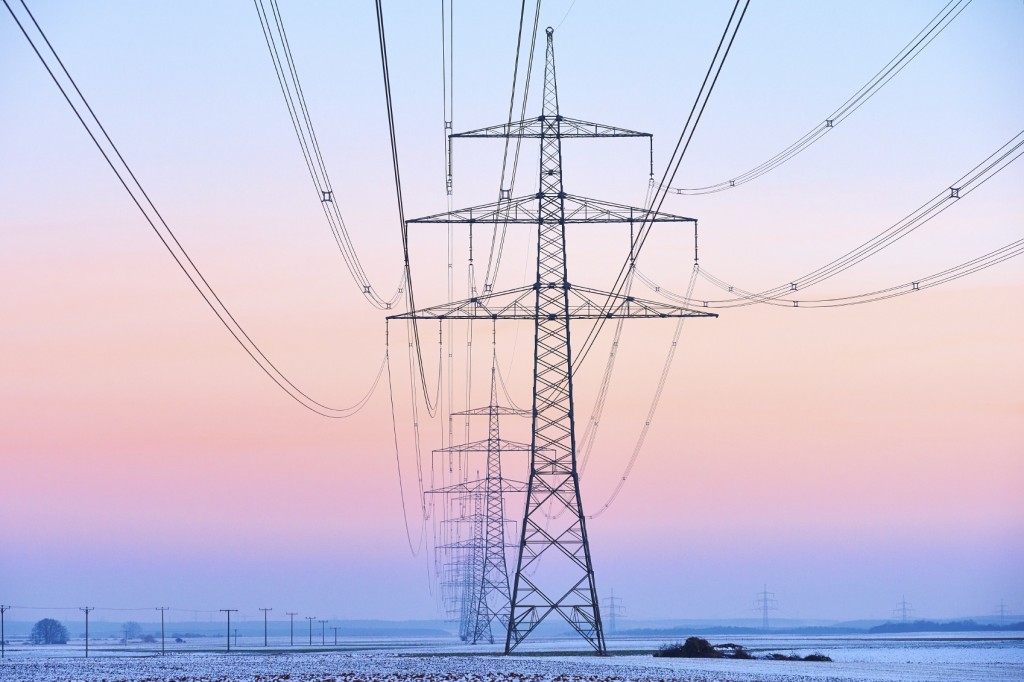
All Aluminum Alloy Conductor (AAAC): Types, Development, Properties and Applications
1. Two Principal Types of AAAC
AAAC conductors are primarily classified based on their alloy composition, with 1120 and 6201 being the most widely used grades:
AAAC 1120
Alloy Composition: Essentially commercially pure aluminum (99.2% minimum purity) with minimal alloying elements.
Key Characteristics:
--Highest electrical conductivity among AAAC grades (≥61% IACS)
--Excellent corrosion resistance due to high aluminum purity
--Lower tensile strength compared to 6201 alloy
Applications:
--Low-voltage distribution lines
--Urban overhead networks
--Secondary transmission lines with shorter span
AAAC 6201
Alloy Composition: Aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloy (Mg: 0.6-0.9%, Si: 0.5-0.9%) with trace elements.
Heat Treatment Variants:
--6201-T81: High-strength variant with tensile strength up to 330 MPa, achieved through solution heat treatment, cold working, and artificial aging
Key Characteristics:
--Balanced strength and conductivity
--Superior sag performance compared to ACSR conductors
--Excellent resistance to stress corrosion cracking
Applications:
--High-voltage transmission lines (110kV and above)
--Long-span crossings
--Coastal and industrial environments with harsh conditions
2. Development of AAAC
The evolution of AAAC reflects the industry's pursuit of more efficient and sustainable power transmission solutions:
Historical Timeline
Technological Advancements
Alloy Optimization: Precise control of magnesium and silicon ratios to balance strength and conductivity
Heat Treatment Innovations: T81 and T83 tempering processes that create fine Mg₂Si precipitates for strength enhancement
Stranding Technologies: Multi-layer stranding designs
Quality Control: Advanced testing methods ensure consistent performance across production batches
3. Design
AAAC conductors is optimized for both mechanical and electrical performance:
Structural Design
Strand: Available in single-layer and multi-layer concentric stranding
Core Structure: No steel core – all strands consist of homogeneous aluminum alloy
Diameter Range: cross-sections from 10 mm² to 930 mm²
Strand Lay Ratio: Scientifically calculated to balance flexibility and tensile strength
Material Components
Alloy Wire: Primary component, available in both 1120 and 6201 alloys
4. Properties of AAAC – Strengths
AAAC offers a unique combination of properties that make it superior to traditional conductors in many applications:
Mechanical Strengths include High Tensile Strength(6201-T81 achieves up to 330 MPa) 、Excellent Sag Performance、Fatigue Resistance
Electrical Strengths include High Current Capacity, Good Conductivity, Corrosion Resistance
Environmental & Economic Strengths include Lightweight, Low Maintenance: Reduced corrosion , extends service life, Cost-Effective: Generally 20-30% lower material cost
5. Application Scenarios for AAAC
AAAC's versatile properties make it suitable for diverse power transmission applications:
Primary Application Areas
1.
--High-Voltage Transmission Lines
2.
--Ideal for 110kV to 1000kV networks
--Preferred for long-distance energy transmission projects
3.
--Coastal and Industrial Environments
6.Global region
Asia-Pacific
North America
Europe
Middle East
The continued development of AAAC technology, including higher strength alloys and improved manufacturing processes, ensures its growing importance in the global transition to more efficient and sustainable power transmission systems.

1. Two Principal Types of AAAC
AAAC conductors are primarily classified based on their alloy composition, with 1120 and 6201 being the most widely used grades:
AAAC 1120
Alloy Composition: Essentially commercially pure aluminum (99.2% minimum purity) with minimal alloying elements.
Key Characteristics:
--Highest electrical conductivity among AAAC grades (≥61% IACS)
--Excellent corrosion resistance due to high aluminum purity
--Lower tensile strength compared to 6201 alloy
Applications:
--Low-voltage distribution lines
--Urban overhead networks
--Secondary transmission lines with shorter span
AAAC 6201
Alloy Composition: Aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloy (Mg: 0.6-0.9%, Si: 0.5-0.9%) with trace elements.
Heat Treatment Variants:
--6201-T81: High-strength variant with tensile strength up to 330 MPa, achieved through solution heat treatment, cold working, and artificial aging
Key Characteristics:
--Balanced strength and conductivity
--Superior sag performance compared to ACSR conductors
--Excellent resistance to stress corrosion cracking
Applications:
--High-voltage transmission lines (110kV and above)
--Long-span crossings
--Coastal and industrial environments with harsh conditions
2. Development of AAAC
The evolution of AAAC reflects the industry's pursuit of more efficient and sustainable power transmission solutions:
Historical Timeline
Technological Advancements
Alloy Optimization: Precise control of magnesium and silicon ratios to balance strength and conductivity
Heat Treatment Innovations: T81 and T83 tempering processes that create fine Mg₂Si precipitates for strength enhancement
Stranding Technologies: Multi-layer stranding designs
Quality Control: Advanced testing methods ensure consistent performance across production batches
3. Design
AAAC conductors is optimized for both mechanical and electrical performance:
Structural Design
Strand: Available in single-layer and multi-layer concentric stranding
Core Structure: No steel core – all strands consist of homogeneous aluminum alloy
Diameter Range: cross-sections from 10 mm² to 930 mm²
Strand Lay Ratio: Scientifically calculated to balance flexibility and tensile strength
Material Components
Alloy Wire: Primary component, available in both 1120 and 6201 alloys
4. Properties of AAAC – Strengths
AAAC offers a unique combination of properties that make it superior to traditional conductors in many applications:
Mechanical Strengths include High Tensile Strength(6201-T81 achieves up to 330 MPa) 、Excellent Sag Performance、Fatigue Resistance
Electrical Strengths include High Current Capacity, Good Conductivity, Corrosion Resistance
Environmental & Economic Strengths include Lightweight, Low Maintenance: Reduced corrosion , extends service life, Cost-Effective: Generally 20-30% lower material cost
5. Application Scenarios for AAAC
AAAC's versatile properties make it suitable for diverse power transmission applications:
Primary Application Areas
1.
--High-Voltage Transmission Lines
2.
--Ideal for 110kV to 1000kV networks
--Preferred for long-distance energy transmission projects
3.
--Coastal and Industrial Environments
6.Global region
Asia-Pacific
North America
Europe
Middle East
The continued development of AAAC technology, including higher strength alloys and improved manufacturing processes, ensures its growing importance in the global transition to more efficient and sustainable power transmission systems.

Next article: